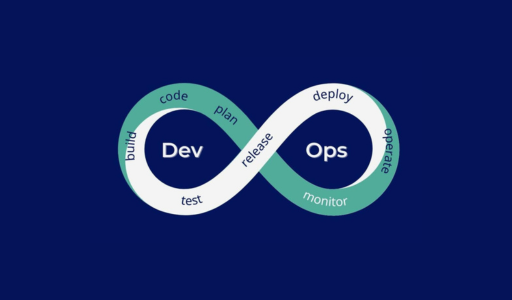
This course is part of our elite learning catalog and is widely chosen by global organizations to train their technical teams.
- Home
- About Us
- Professional Courses
Professional Courses
Programming Training
Full Stack Training
Mobile App Training
Cyber Security Training
Networking Training
DB Management Training
Software Test Training
Data Science & Analyst
Cloud Computing Training
Crash Courses
Programming Training
Business Management
Testing Training
Security Training
Digital Marketing Training
DB Management Training
- Turbo Courses
Slash Courses BUDGET
Classic Courses BUDGET
- Support
- Contact Us